Call us Monday to Friday, 9am to 5pm:
📞 +32 471 36 77 09
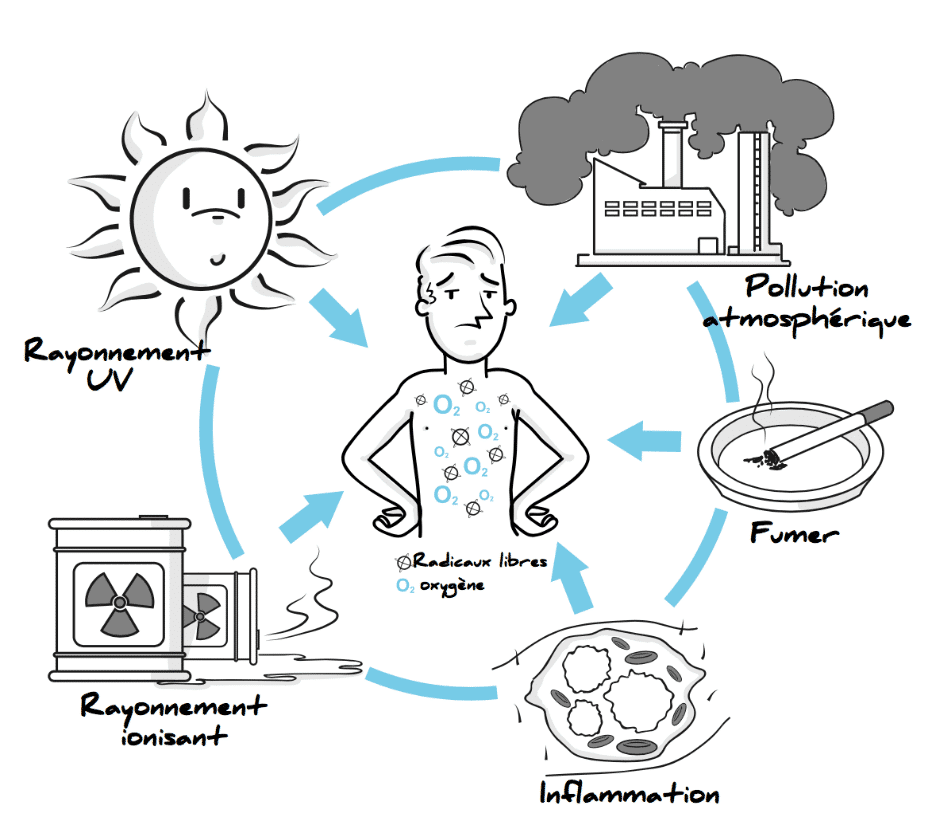
Visit free radicals are formed naturally in our bodies during normal metabolic processes, such as breathing. However, their production can be amplified by external factors such as exposure to ultraviolet rays, pollution, smoking and stress.
Free radicals are formed by losing an electron, making them unstable and highly reactive. They then seek to compensate by stealing the missing electron from other molecules, triggering potentially damaging chain reactions.
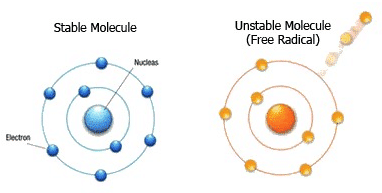
In excess, free radicals cause cancer. oxidative stress can damage essential cellular components such as proteins, lipids and DNA, contributing to premature aging of the skin and the development of various diseases.

To counteract these harmful effects, the body uses antioxidants. Antioxidants neutralize free radicals by donating an electron, thus stabilizing these unstable molecules. It's important to note that antioxidants themselves remain stable after donating an electron, enabling them to play their protective role without in turn becoming free radicals.
Maintaining a balance between free radicals and antioxidants is crucial to health, as an excess of free radicals can lead to oxidative stress, responsible for cell damage. Adopting a diet rich in antioxidants and a healthy lifestyle helps preserve this balance and protect the body against the damaging effects of free radicals.
Just as the body produces free radicals, it also naturally produces its own endogenous antioxidants. To achieve the right balance, the body supplements itself with antioxidants through diet and water.
Antioxidants such as vitamins C and E, selenium and beta-carotene are found in a variety of fruits and vegetables. They play an essential role in neutralizing free radicals, protecting cells against oxidative stress. What's more, some of these antioxidants are essential nutrients for the body to function properly.
Hydrogenated water is enriched with molecular hydrogen (H₂), a gas with antioxidant properties. Molecular hydrogen is able to rapidly penetrate cell membranes due to its small size, reaching areas that other antioxidants might not. Whereas dietary antioxidants neutralize free radicals by surrendering an electron to them, molecular hydrogen acts by reacting directly with hydroxyl radicals to form water, thus reducing oxidative stress without producing potentially harmful by-products.
In conclusion, a diet rich in natural antioxidants is essential to provide the body with the nutrients it needs to function properly and protect against oxidative stress. Consumption of hydrogenated water can offer complementary benefits by specifically targeting certain free radicals and boosting endogenous antioxidant defenses.
At Aquacycle.euwe opted for the molecular hydrogen dynamizationThis technology transforms water into a powerful antioxidant through electrolysis. This process, also known as hydrogenation or ionizationworks by applying a low-intensity electric current that separates hydrogen and oxygen atoms from certain water molecules.
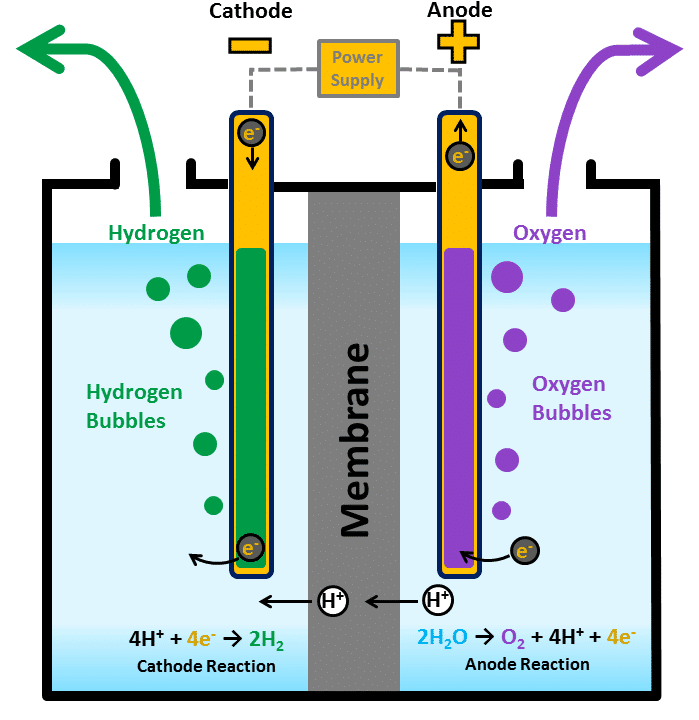
The resulting chemical reaction produces a water highly antioxidantwhich neutralizes the free radicals responsible for oxidative stress.
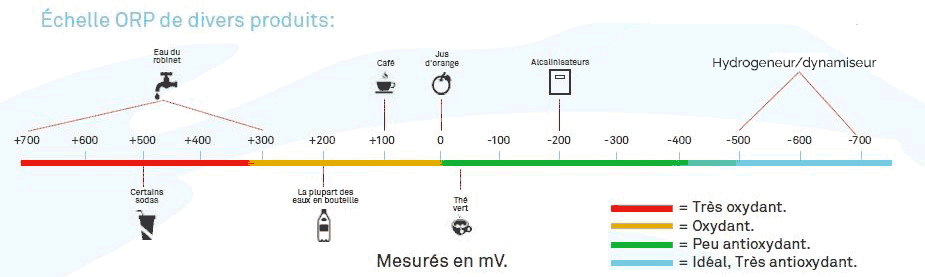
The redox potential, often abbreviated to ORP (Oxidation-Reduction Potential), is a measure of the tendency of water to gain or lose electrons. Expressed in millivolts (mV), ORP indicates the oxidizing or reducing capacity of a medium. The higher the ORP value, the more oxidizing the medium; conversely, a negative value indicates an antioxidant medium. This measurement is commonly used to assess water quality.
Researchers recommend a dose of 1 to 2 mg/day. This means you can drink 1 to 2 liters of water a day with a dissolved hydrogen concentration of 1.0 ppm, preferably on an empty stomach and between meals.
Consumption of hydrogenated water is generally considered safe, and no notable side effects have been reported to date. Molecular hydrogen (H₂) is a light molecule which, after exerting its antioxidant action, is rapidly eliminated from the body through respiration or urine. Even in the event of heavy consumption, excess hydrogen is naturally expelled without accumulating in the body.
It is important to note that the long-term effects of regular consumption of hydrogenated water have not been sufficiently studied. It is therefore advisable to inform your doctor if you are considering incorporating hydrogenated water into your daily routine.
In addition to direct consumption, dynamized water can also be used for other applications. In the same way that it stabilizes free radicals in our bodies, it can also stabilize them during :
Washing your fruit and vegetables in hydrogenated water is an excellent way of removing traces of pesticides/herbicides.
If your lifestyle exposes you to oxidative stress (pollution, tobacco, alcohol, unbalanced diet, intense physical activity, stress...) and your fruit and vegetable intake is insufficient, a water energizer can be an essential ally in protecting your health and limiting cellular aging.
Choose pure water revitalized Combine an osmosis unit and a dynamizer for top-quality hydration and optimal well-being!